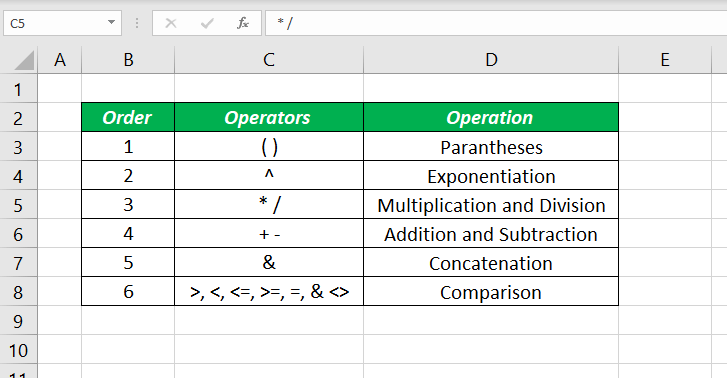
Microsoft Excel evaluate the formulas from Left to Right following a particular Operator precedence.
- Parentheses ‘( )’ are evaluated at first,
- then Exponentiation ‘^’,
- Multiplication or Division ‘* or /’ (whichever comes first),
- Addition or Subtraction ‘+ or -’ (again whichever comes first),
- then Concatenation (joining strings) ‘&’
- and finally Comparison.
For example, while evaluating the formula =4+5*2, Excel multiplies 5 by 2, then add that result to 4.
i.e. 5 * 2 which is 10 will be added to 4
=4+5*2
=14
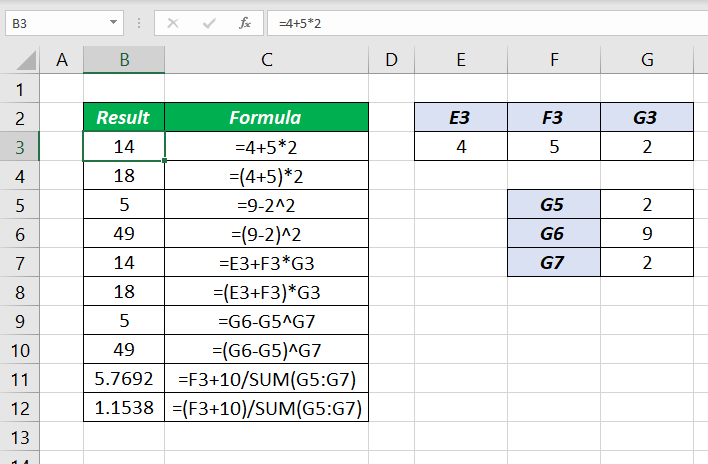
But when Parentheses are added around 4+5, that segment is evaluated first and that result is multiplied by 2.
i.e. 4+5 which is 9 will be multiplied by 2.
=(4+5)*2
=18