Table of Contents
Introduction to VBA for Excel
VBA stands for Visual Basic for Applications. It is a custom version of the Visual Basic programming language that has powered Microsoft Excel’s macros since the mid-1990s. The programming interface of MS Excel will let you,
- Create and Execute Macros (explained in the next section). Anything that the user can do in Excel from the user interface can be done by writing code in VBA for Excel.
- Create User Defined Functions (UDFs).
- Integrate Excel with other applications such as Microsoft Word, PowerPoint, Outlook, Notepad, etc.
What is a Macro ?
Macros are codes written in VBA (Visual Basic for Applications), or recorded in MS Excel (or other MS applications) which helps to reduce the manual effort required for a job. Macros save your time and headaches by automating common, repetitive tasks. They reduce the possibility of human error that increases with many, repetitive keystrokes and tasks. The most important feature of an Excel macro is, it can be saved for future use, shared among multiple users.
In a layman’s language, a macro is a recording of your routine steps in Excel that you can replay using a single button
The best part is You don’t have to be a programmer or know Visual Basic Applications (VBA) to use Macros. You just need to copy the codes shared here and hit the run button to execute them. Save the file as a Macro enabled workbook for future use.
How to use the codes shared here?
- Step 1: Copy the Code.
- Step 2: Go to the Developer tab of the Excel ribbon and Click on Visual Basic to activate the Visual Basic Editor of Excel. ‘ALT + F11’ is the keyboard shortcut for the Visual Basic Editor.
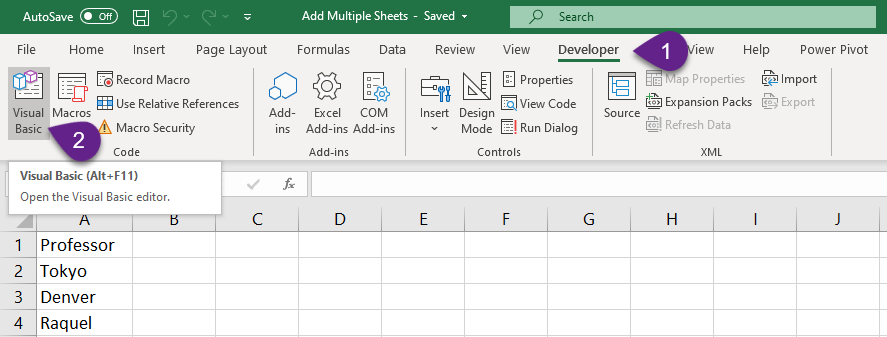
- Step 3: Right click on the tree view and select Insert to insert a new ‘Module’.
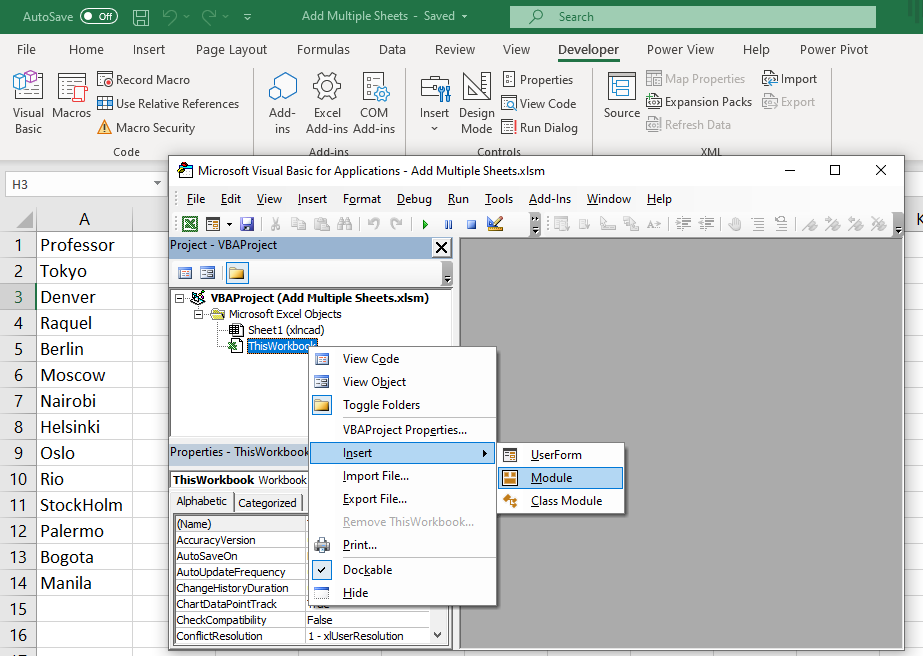
- Step 4: Paste the copied code into the newly inserted module.
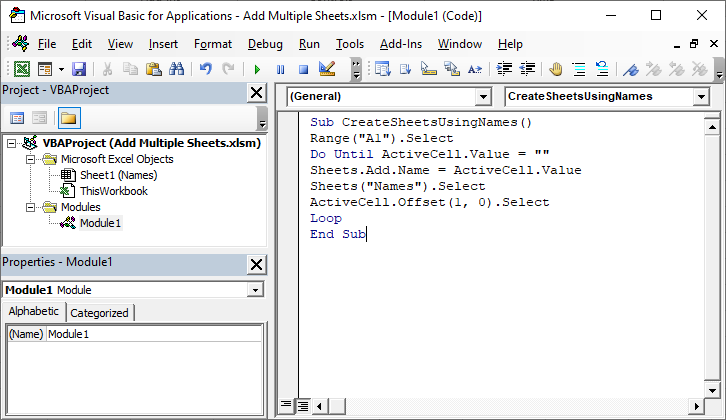
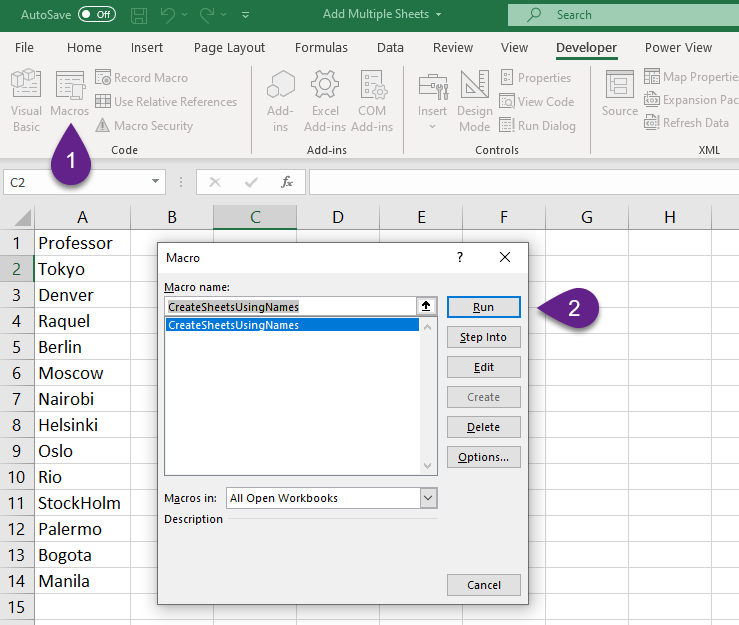
- Step 5: Close the VB editor and Click on Macros in the Developer Tab. You will get a dialogue box with the list of Macros ready for execution. Click on the Run button to execute the macro.
Ready to use Macros
1. Add Multiple WorkSheets in a Workbook
2. Delete Worksheet/Worksheets
3. Insert Rows
4. Delete Rows
5. Macros to Insert and Delete Columns
6. Message Box and Input Box in VBA
7. Import and Export Text Files into Excel
8. Hide and Unhide Worksheets
9. Convert a worksheet into Very Hidden Mode
10. Delete every Worksheet, except Active Sheet
11. Create a PDF file from a worksheet
12. Convert Text into Upper, Lower or Proper Case
13. Join Text in Rows and Columns
14. Hide and UnHide Rows and Columns
15. Select the first 1000 cells of Column A
16. Protect and UnProtect sheets with Password
17. Text to Speech
18. AutoFit Rows and Columns
19. Reverse Text
20. Macro to convert Formulas into Values
21. Create a List of Worksheets
22. Count the number of worksheets in a workbook
23. Convert Numbers into Words
24. Split Data into Rows or Columns
25. Macro to create an Excel Table
26. Find and Highlight the Largest and Smallest numbers in a data set
27. Find and Highlight the Negative and Positive values
28. Italicize a specific row of every worksheet
29. Remove Data Validation
30. Select the First or Last worksheet
31. Create the list of Files and Subfolders
32. Sort worksheets in Alphabetical order
33. Rename every worksheet in a workbook
34. Macro to create Pivot Table
35. Close Workbooks
36. Group workbooks
37. Create a Workbook for every Worksheet
38. Create the Table of Contents
39. Create a copy of the Workbook with a Time stamp
40. Combine different workbooks
41. Activate the Data Form in Excel
42. Hide formulas in a worksheet
42. Highlight misspelled words
43. Delete blank worksheets
44. Delete Pivot tables
45. Open office Apps from Excel
46. Send workbook as mail through Outlook
47. Resize charts in a workbook
48. Highlight cells containing a specific Text
49. Delete Files and Directories from Excel
50. Create a picture of the selection
51. Perform arithmetic operation to a selection
Things to remember while using Macros
- By default, the tab for developers is not displayed in excel. If you can’t see the Developer tab, use the quick access toolbar to activate it.
- By default, Macros are disabled in excel. To execute macros, you will need to enable running macros.
- We cannot Undo an action performed using Macro. Make sure that you have a backup of the data before executing the macro.
- To save macros in a workbook, you must save your workbook in a macro-enabled format *.xlsm
- Always fill in the description of the macro when creating one. This will help you understand your own work if you have to revisit it weeks or months later.